FDM 3D Printing:
Guide to Economical and Reliable 3D Printing
What is FDM technology?
The Fused Deposition Modeling FDM technology 3D printing is the most popular method worldwide, due to its low cost and ease of use....
The process is based on melting and depositing thermoplastic material layer by layer, creating durable and functional objects for a variety of applications.
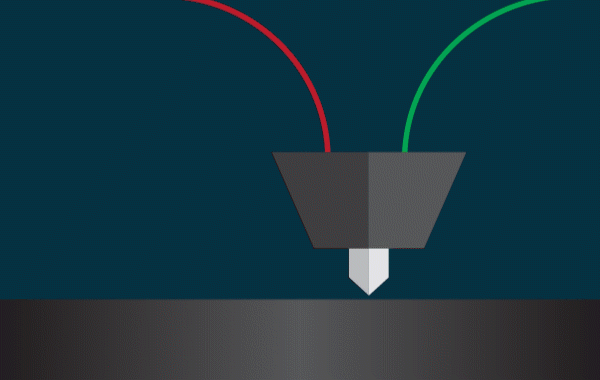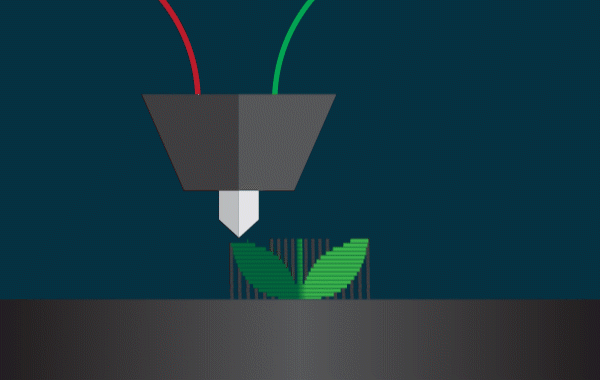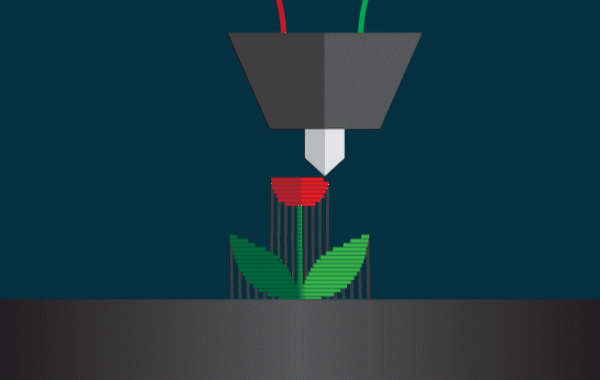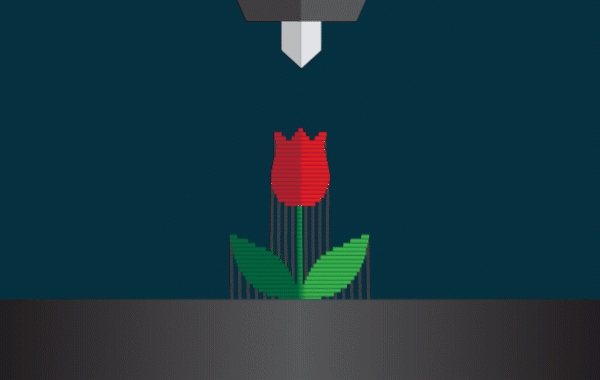
How the technology works FDM;
Printing begins with the digital 3D model (usually an STL or OBJ file). Using slicing software, the model is “cut” into horizontal layers, while the printer follows instructions to deposit material exactly where needed.
Basic materials used in FDM 3D Printing
The variety of materials makes FDM versatile for many uses. The most popular are:
1. PLA (Polylactic Acid)
One of the most popular materials on the market. It is environmentally friendly, easy to print and ideal for prototypes, decorative objects and educational applications.
2. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
More durable than PLA, it withstands higher temperatures and is widely used in industrial components and functional prototypes.
3. PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
Combines the ease of printing of PLA with the mechanical strength of ABS. Ideal for mechanical parts, housings and components that come into contact with food....
4. TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
Flexible and elastic material, suitable for components that require deformation, such as gaskets, protective cases, or anti-slip parts.
5. Nylon (Polyamide)
Extremely resistant to impact, abrasion and chemicals. Used for mechanical parts that are subjected to intense stress.
6. PC (Polycarbonate)
One of the most durable thermoplastics, with very high resistance to heat and mechanical stress. Suitable for industrial applications.
7. Wood-Filled PLA
A PLA material containing wood fibers, giving a wood texture and aroma. Ideal for decorative constructions with a natural look.
8. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Filament
Contains carbon fibers for extra rigidity and strength. Suitable for applications requiring high structural stability and reduced weight.
Advantages of FDM printing
Here’s an indicative pricing of my services
Economic method
Easy to use
Variety of materials
Machine availability σ
Ideal for rapid prototyping
Disadvantages of FDM printing
Here’s an indicative pricing of my services
Lower resolution
Need for supports
Geometry restrictions:
Printing time:
Applications of FDM technology
FDM technology finds application in many areas, such as:
- Industrial design and prototyping
- Educational models and educational institutions
- Functional parts and tools
- Artistic creations and decorative objects
- Personal projects and hobbies

Comparison with other 3D Printing technologies
| Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| FDM | Low cost, easy to use, wide range of materials | Lower resolution, visible layers |
| SLA | High precision and smooth surface | More expensive, more sensitive process |
| SLS | Strong and durable components, without supports | Accurate, requires specialized equipment |
| Metal 3D Printing | Excellent durability and functionality | Very high cost and equipment |

What Applications Does FDM Printing Cover?
The FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) It is ideal for a wide range of applications at both professional and amateur levels:
- Prototypes for initial form and application check.
- Tools and custom jigs for use in production lines.
- Cases and enclosures for electronic or mechanical components.
- Visual models for presentations, exhibitions or promotional material.
- Educational projects in schools and universities, etc.
The ease of production and low cost make FDM technology ideal for rapid product design & testing.

What Materials Are Supported?
The Get 3D offers a wide range of thermoplastic materials suitable for every need:
PLA
Economical, ecological and ideal for prototypes.
TPU
Flexible material for rubber parts.
PETG
Moisture resistant, suitable for mechanical parts.
NYLON
Ideal for parts with abrasion resistance and high load.
ABS
High mechanical strength and heat resistance.
Carbon/ Glass Fiber Blends
Reinforced plastics for increased rigidity.
Depending on your usage and budget, we guide you through the appropriate material selection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What kind of files are needed for FDM printing?
The most common files are STL and OBJ, which come from CAD or 3D modeling programs.
How long does a print take?
The time depends on the size and complexity, from 1-2 hours to days for large items.
Are objects printed with FDM durable?
It depends on the material, but they are generally durable for everyday use, especially with materials like ABS and PETG.
Can FDM print complex designs?
Yes, but supporting structures are required in complex or projecting sections.
Send us/upload your file (.STL / .OBJ) for free estimate or contact our team to find the best solution.
"If you don't have a file, we can create it for you via 3D designing.»
🚀 Start printing your project today!