Virtualize Your Imagination
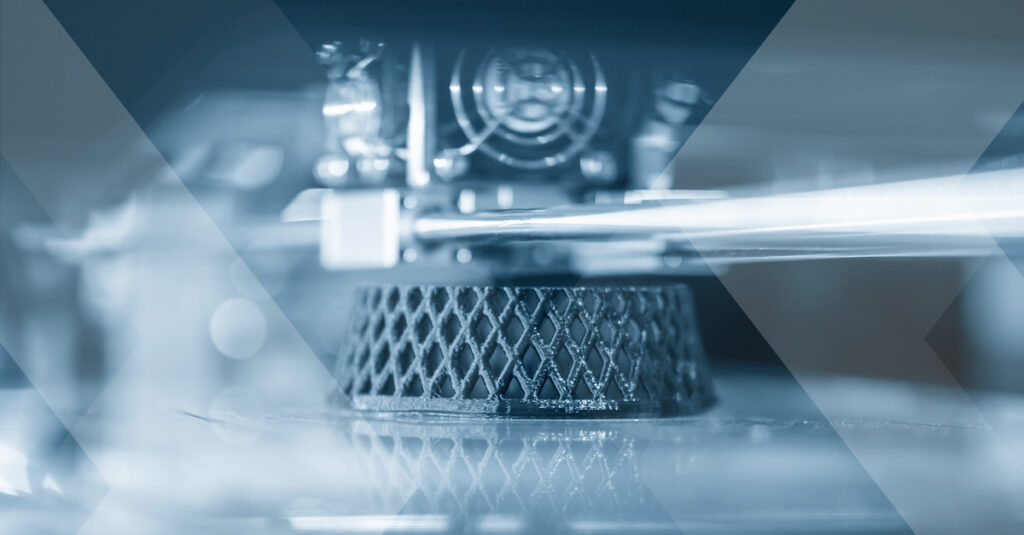

3D Printing (or as formally called Additive Manufacturing) is a new manufacturing method for parts with the cascading deposition of material in layers. The way of material’s deposition differs from method to method and from material to material.
3D Printing was born in decade of 80s with initial known term “rapid prototyping”. It was mainly utilized for the manufacturing of prototypes in a faster and more accurate way compared to traditional manufacturing methods. After 30 years of continuous development, we can now count limitless application of 3d printing. Combination of previous referred advantages and manufacturing low cost with desktop machines produced has driven 3d printing technology “accessible” to most people in the world in a vary short period.
How it works
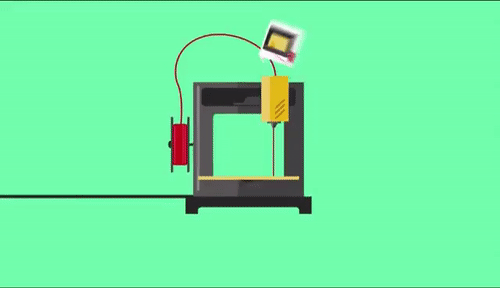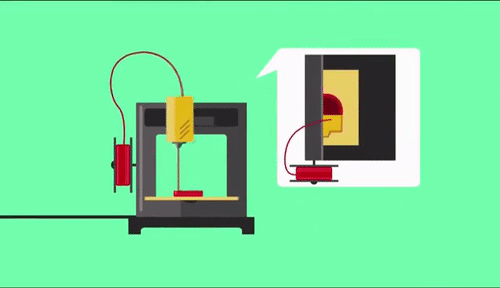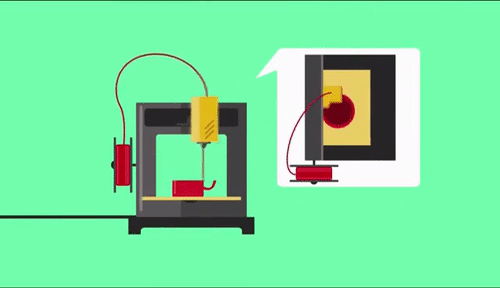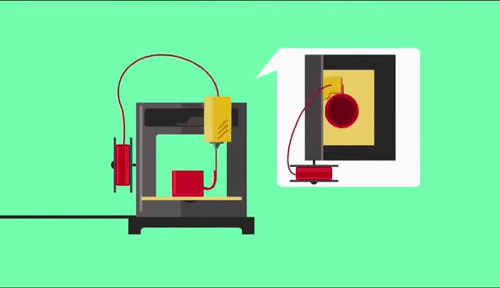
As already referred, the process of 3d printing “builds” in a layer-by-layer way the requested part. Usually materials used are plastics, but this is not necessary, as also metal 3d printing can be utilized. After finishing each layer either bed or the printing head moves vertically to specific position so as to continue with next layer.
What technologies are available?
- FFF/FDM
One of the most known 3d printing technology is FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) which as actually called, plastic is fused through a printing head in high temperatures. 3D printing head is positioned in an X-Y axes moving system which is electronically driven throughout all printing surface (bed). With cooling of printed part, a solidification is forced and after each layer is finished bed is moved downwards. With repeat of the process described above the final product is manufactured.
- SLA
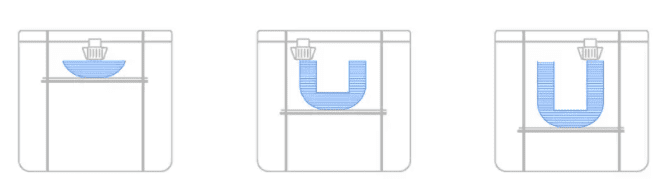
SLA technology utilizes photopolymerized resin as raw material. Resin is pured inside a tank which has a transparent bottom and the build platform merge inside this tank during printing period. A source light (usually used a laser source) is responsible for the polymerization of the resin in order to solidify the part in specific points. The build platform gradually raises (or in some case submerges inside) until the whole z axis of the part is 3d printed.
- DLP
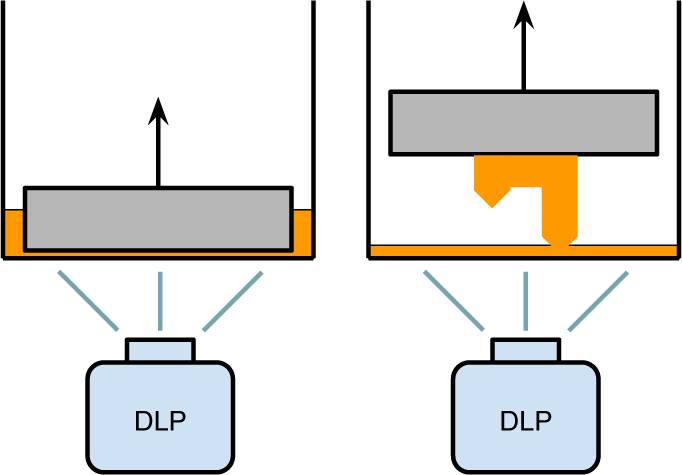
This technology is based on resins just like SLA. Instead of a laser guided to certain points, a projector projects the whole layer making the whole layer solid.
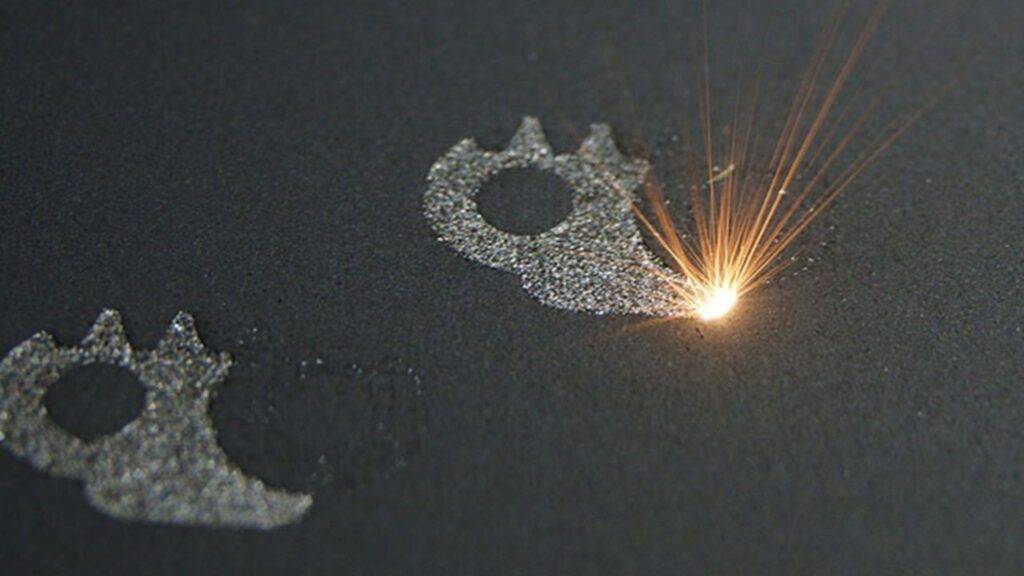
- SLS
SLS technology uses as raw material polymers in powder form. Powder is inside a tank where a roller is responsible for the perfect straightening of the powder layer at the printing surface. A laser head is used for local sintering of the powder so as to create a printed surface. After each layer platform is lowered and the roller creates a new smooth surface of polymer’s powder and the process is repeating until the parts are going to be 3d printed.
- Binder Jetting
This kind of technology has many similarities to this of SLS, but in this case the fusion of the powder is achieved though a chemical bond using the appropriate binder through jet. With binder jet technology and with an appropriate printing head a new possibility to manufacture absolutely colorful 3d prints is created (Color Binder Jet).
- SLM
SLM consists the most widely used technology in metal 3d printing. The operational principle has by far many similarities to SLS, but when 3d printing comes to metals the required power in laser source is higher enough compared to this of polymers one.

Modern method of manufacturing plastics and other products.
Experience in both construction and 3D print
Decision making based in economical profit
Environmental friendly method as the rejected material is too low compared to traditional methods.
